- +91 91000 65552
- +91 9324982134
- contact@respliceinstitute.com
- Mon-sat 10:00 -18:00
Think of chemotherapy like a war. It’s the kind that doesn’t just shake up your body—it rattles your cells, nerves, bones, and sometimes even your spirit. The cancer might be gone, but the body’s battlefield still carries scars, broken walls, and shaky systems. Post-chemotherapy secondary prevention is that calm after the storm—it’s the blueprint for rebuilding.
This isn’t about avoiding cancer altogether—that’s primary prevention. Secondary prevention is the step that comes after the fight: detecting risks early, reversing the damage, and supporting every part of you—physically, emotionally, and mentally—to feel whole again.

Let’s say your body is a city. Chemotherapy was the emergency demolition to get rid of the bad guys. But once they’re gone, the roads are cracked, the traffic lights don’t work, and power flickers. That’s what chemo leaves behind—cellular damage, inflammation, immune suppression, brain fog, and even gut imbalance. Now begins the restoration.
More than 60–70% of cancer survivors experience symptoms that last beyond the treatment phase. These can range from nerve pain and memory issues to digestive problems and emotional exhaustion. Ignoring them is like patching a leak with chewing gum—it might hold, but not for long.
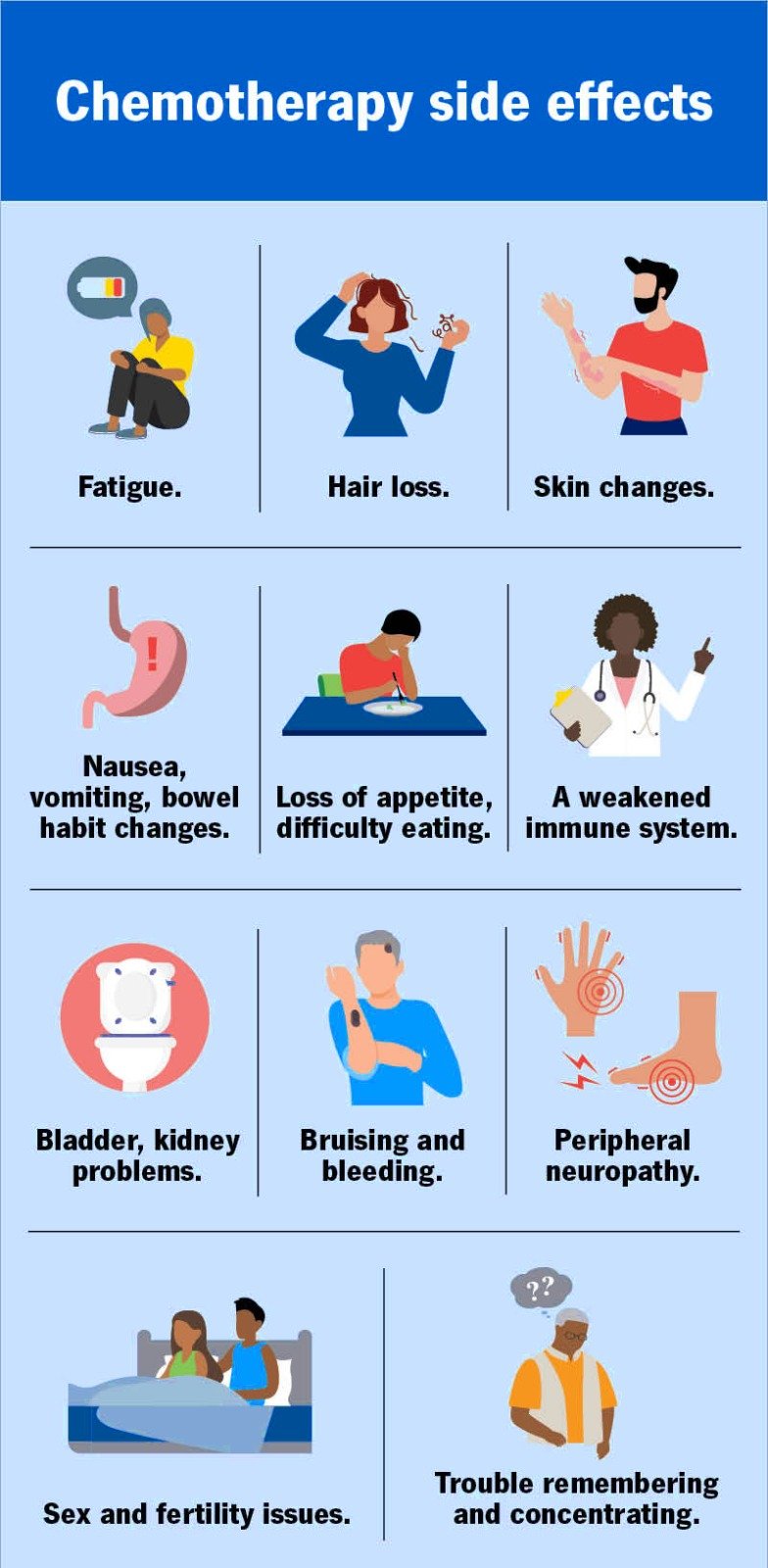
Here’s how your body might signal that it’s not fully okay—even when the cancer’s gone.
These aren’t minor side effects. They’re reminders that your internal systems need attention. Especially your gut microbiome—that invisible jungle of bacteria in your belly that affects everything from digestion to immunity to mental clarity.
Chemo wipes out the good bacteria along with the bad. This creates gut dysbiosis, where harmful microbes flourish and cause inflammation, poor digestion, and lowered immunity.
Many experience chemo brain: forgetfulness, slow thinking, zoning out in the middle of a conversation.
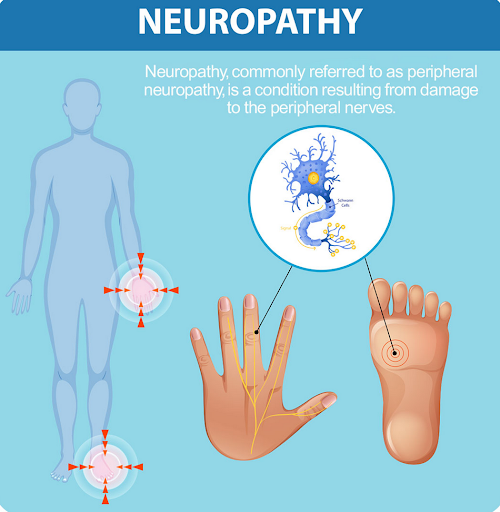
Numb toes, tingling fingers, or weird electric jolts? That’s peripheral neuropathy.
Imagine your personal defense force is down to a handful of sleepy soldiers.

From early menopause to thyroid issues and adrenal fatigue, your hormones often go out of sync.
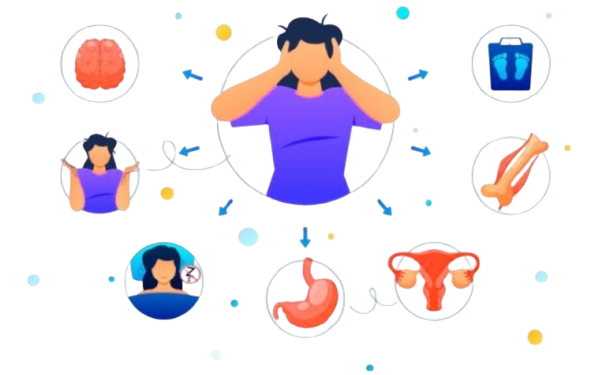
Recovery isn’t just medical. It’s emotional too. The mental exhaustion, fear, and confusion post-treatment are very real.
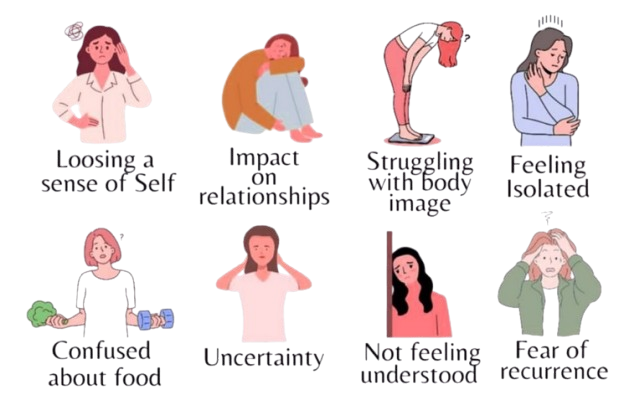

These are doctor-approved, time-tested therapies that offer a structured path to recovery:
Many hospitals now include secondary prevention as part of survivorship care plans. But for holistic healing, newer approaches are helping fill in the gaps.

Healing doesn’t always follow just one path. Here are some options gaining attention:
But one therapy, in particular, is standing out for survivors battling gut issues, emotional changes, and low energy: Gut Microbiota Transplantation.
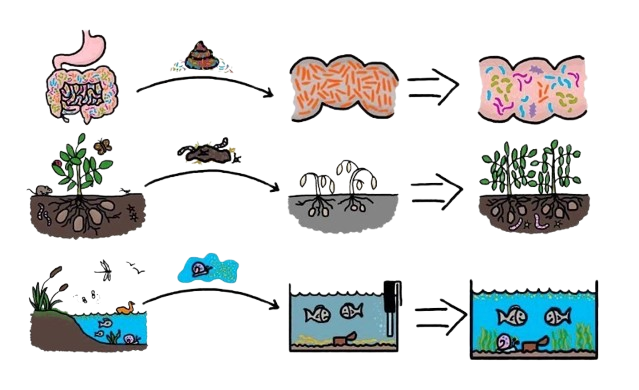
Chemo wrecks the gut. It’s like bulldozing a garden to remove a single weed. You’re left with dry soil, no nutrients, and harmful bugs taking over.
Gut Microbiota Transplantation or FMT is like replanting that garden with rich, healthy soil. A healthy child under 12 years of age is selected as a donor and good bacteria are transferred from the doner to the patients intestine. At places like Resplice Research Institute, this is done under strict safety, screening, and hygiene standards.
Here’s what makes GMT at Resplice different:
Benefits seen post-GMT:
Think of GMT as hitting the refresh button on your inner ecosystem.
Here’s what the numbers say:
Recovery needs vary by age and gender. For instance, younger survivors report more intense symptoms. Women, especially, show a higher risk for immune complications and emotional effects.
Cancer may be the main villain, but the fallout of its treatment can create silent struggles that stretch for years. Post-chemotherapy secondary prevention isn’t about being cautious—it’s about being smart. It’s about healing the invisible wounds, rebuilding the body’s internal scaffolding, and giving survivors the dignity of complete recovery.
This healing journey can involve conventional treatment, ancient healing systems, or cutting-edge science like Gut Microbiota Transplantation. What matters is not choosing one over the other—but choosing what helps you feel whole again.
Your body’s story didn’t end with chemo. In many ways, it’s just beginning.
It's the phase after the cancer battle, where we focus on rebuilding what chemo broke—your cells, immunity, digestion, nerves, and emotions. It's not about avoiding cancer again, but about detecting, repairing, and supporting your body for full recovery.
Because chemo is like a storm—it clears out the threat but leaves damage behind. Lingering fatigue, brain fog, nerve pain, or emotional shifts are signs that your internal systems are still healing.
Survivors often experience:
FatigueThese are signs your body is still patching itself up.
Chemo brain feels like mental static—forgetfulness, zoning out, losing your train of thought. It can last months or years, but therapies like neurofeedback, GMT, and cognitive rehab can help sharpen your focus again.
Think of your gut as a garden. Chemo doesn’t discriminate—it bulldozes the weeds and flowers alike. This gut damage, known as dysbiosis, affects your immunity, digestion, and even mental health.
You might experience:
Bloating, constipation, or diarrheaIncreased food intolerances
Lowered immunity
Brain fog or anxiety
Your gut may be crying for help long after your body seems fine.
GMT is like replanting a damaged gut garden with healthy soil. Good bacteria from a screened, healthy donor (usually a child under 12) are transplanted into your colon to restore balance, immunity, and digestion.
Gut dysbiosis means there’s an imbalance in good and bad bacteria. In IBD, this imbalance can worsen inflammation, symptoms, and even affect mood. Restoring balance is a key treatment goal.
When done at certified centers like Resplice Research Institute, GMT follows strict hygiene, screening, and sterile processing protocols. Only young donors are chosen, ensuring a clean and resilient microbiome.
Many survivors report:
Better digestion and sleepLess fatigue
Improved mental clarity
Reduced anxiety and mood swings
Stronger immune response
It acts as a reset button for your inner world.
They support organ systems weakened by chemo. Examples include:
Pain meds for nerve issuesCardiac care and bone scans
Mental health therapy
Supplements for nutrient losses
These are often part of a Survivorship Care Plan.
Yes. While not replacements for medical treatment, they offer support by:
Rebalancing hormones (Ayurveda)Detoxifying the body (Naturopathy)
Calming the nervous system (Yoga, Pranayama)
Personalizing care (Functional Medicine)
If you feel persistently tired, emotionally off, unable to digest food well, or mentally foggy, it’s likely your body needs deeper support. Don’t ignore subtle signals—they’re messages, not overreactions.
Women may face early menopause, hormonal shifts, and stronger immune dysregulation. Younger survivors report more intense fatigue and emotional effects. Each body's story is different, and recovery needs must be tailored accordingly.
There’s no fixed time. Some recover in months, others take years. What matters is steady healing, guided support, and listening to your body without guilt or comparison.
Absolutely. Healing is not one-size-fits-all. You can blend medical care with Ayurveda, GMT, Yoga, or neurotherapy. The goal isn't picking sides—it's picking what makes you whole again.

Resplice Institute is India’s first integrated center offering autism therapy, gut microbiome treatment, and preventive health planning. We combine science and empathy to heal lives from the root.
© 2025 respliceinstitute.com || All Rights Reserved